Applications and Types of Printed Circuit Board
It is crucial to understand the distinction in between PCB production and its assembly procedure.
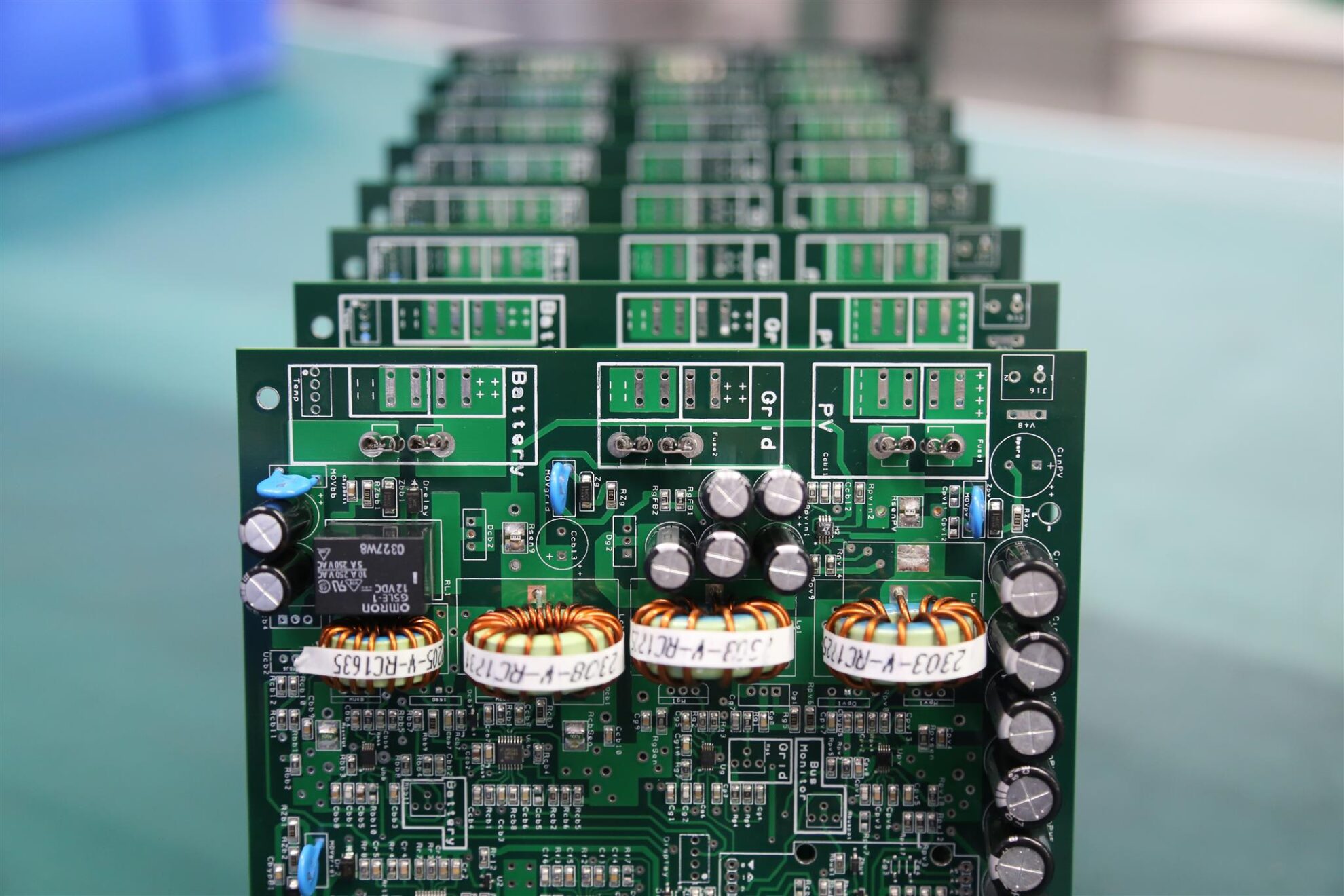
Table of Content
What Are the Different Types and Applications of PCAs?
A printed circuit board is commonly used in electronic products as a base for wiring and socket
components that are mounted on the surface.
Photolithography is used to create PCBs in applications that require fine wiring such as computer
systems. This process is a scaled up version of the way connections are made on processors.
Solder is used by machines to attach electronic devices to the PCB. In an industrial microwave, the PCB
is heated to melt the solder connecting the components. The majority of PCBs consist of glass-reinforced
or fiberglass polymers and copper traces.
PCBs used for simple electronic devices have a single layer. Up to 12 layers can be found on complex
electronic printed circuit boards such as motherboards or digital graphics cards. PCBs can be any color,
including green.
PCBs connect electrical components using copper tracks, unlike ordinary wires. Electrical components are
secured by drilling holes into the board. Soldering is used to secure them, and copper tracks are used
to connect them into a circuit. A PCB assembly is the combination of a PCB (printed circuit board) and
its components. The PCB would be a useless board without this assembly. Its importance is obvious.
PCBs can be found in nearly all electronic devices that we use and see every day. These PCBs are
responsible for making devices that we use every day look smaller, while still containing more
technology. Applications include:
• Radios and TVs
• Computers
• Alarm systems
• Coffee Machines
• Washing machines
• Playstations are a great way to play games.
• Mobile phones
• Ovens
The other application areas include medical and industrial components, as well as military (bikes,
automobiles, planes, etc.).
Overview of PCB Manufacturing Process
Understanding the differences between PCB assembly and PCB manufacturing is essential. PCB assembly
production involves PCB design, prototyping and PCB mounting.
We will now take a closer look at PCB production.
Board design, component procurement and assembly are the three main PCB manufacturing processes. Design
for testability (DFT), and design for manufactureability (DFM) is essential to ensuring the best return
on the project costs, whether the PCB production and assembly is for large or small batches. Assembly of
a PCB can vary, unlike manufacturing. It depends on your preferences or application.
related Posts
Contact us
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Teams: alek_youte
Email: sales@yt-electronic.com