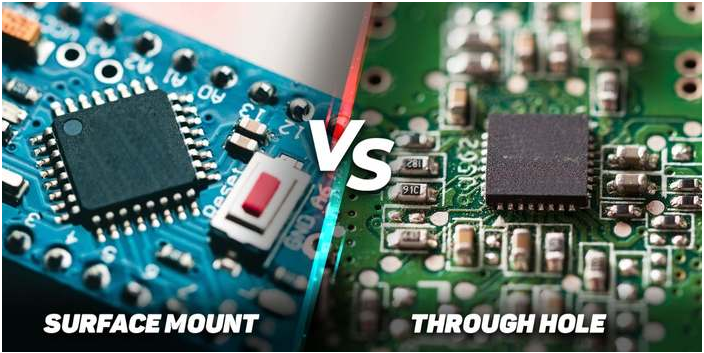
Surface mount technology and through-hole traditional technology are the two most common component assembly methods in electronic product assembly.
The two are very different in terms of substrates, components, assembly processes etc. This leads to different performance and applications characteristics.
SMT vs THT -- Fundamental Difference
Surface mount technology differs from through-hole technology in the way that components are assembled.
Surface mount technology involves mounting components directly onto the PCB using a pick-and-place machine. THT involves inserting leaded components through the holes in the PCB.
Process Characteristics of SMT
These components are compact and light, which allows for a reduction in PCB weight and space.
Electronic products that are more integrated can be made with a high assembly density.
It is a high-volume, automated PCB assembly machine with high production efficiency.
Process Features of THT
The components are heavy and large, which requires more PCB weight and space.
The assembly density is low and it's difficult to produce highly integrated electronic products.
Production efficiency is low, and manual work is required.
Specific Differences Between THT and SMT
The following differences exist between SMT & THT:
Substrate:
Surface mount technology PCBs need to have reserved pads while THT PCBs require through-holes.
Components:
Sheet components are used in SMT, while lead components are used in THT.
Component Form:
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) places the components and the solder joints on the same plane. THT, on the other hand, has the components and the solder joint on both sides.
Solder Joint Shape:
Solder joints for SMT technology are oval or round, whereas solder joint through-hole technologies are diamond or rectangular.
Assembly Process Method
Surface Mount Technology uses a place-and-reflow machine, whereas Through-Hole Technology uses a plug in machine and a Wave Soldering Oven.
Performance and Application Characteristics SMT and THT
The performance and application characteristics of the SMT process and THT are different.
1) SMT Process: Performance Advantages
Surface mount technology has a number of performance advantages.
Small components and lightweight: The components used in SMT are small, lightweight and can save PCB weight and space.
Electronic products that are lightweight, thin, and portable have a lot to gain.
High Assembly Density: The SMT technology allows for a higher component assembly density. This results in more integrated electronic products.
Electronic products that are aimed at high performance and functionality should be considered.
High efficiency production: The SMT process allows for automated mass production. This improves production efficiency while reducing costs.
2) Application Characteristics of the SMT Process
SMT is widely used in the consumer electronics, communications equipment and other fields because of its high integration and production efficiency.
SMT is used in almost all electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops and other products.
3) The THT Process Has Performance Advantages
Performance advantages of THT are mostly in the following areas:
High mechanical resistance: Both sides of the PCB are made of high-strength material, with components and solder joints located on the PCB.
High reliability: The THT process uses molten solder which is highly reliable.
This is especially important for electronic devices that must work in harsh environments.
4) Application Characteristics of the THT Process
THT is still in demand for automotive electronics, as it has good mechanical strength. In the automotive electronics, for example, parts must be able to withstand vibration and impact. Through-hole technology is used.
Future Development of SMT & THT
Surface Mount Technology will become more popular in the future with the development of electronic devices.
The cost of SMT will decrease as technology improves, making it a more competitive process.
THT will continue to have applications in certain fields but will be gradually limited.









